Cotton Slippers
Exclusive Slipper Design to boost your business
Your Trustful Cotton Slippers Supplier
Ningbo Cotton Slipper Co., Ltd Is One Of Slippers Manufacturers In China Since 2019. As A Leading Professional China-Slipper Factory , Our Company Manufacturing Cotton Slippers, Slides, Clogs, Linen Slippers Etc. With Own Design Team To Ensure Exclusive Style. Contact Us Today To Request A Free Quote Or More Information.



REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS

Step 1: Buy Material
- Choose suitable cotton fabrics, based on comfort, durability, and price.
- Source other materials, like rubber or EVA for soles, thread, and glue.

Step 2: Fabric pretreatment
- Wash and pre-shrink fabric so it doesn’t shrink when you make slippers.
- Dye or print the fabric to the desired color or pattern.

Step 3: Cutting
- Cut fabric into pieces for the upper and lining with a cutting machine or automatic cutter.
- Cut the insole and sole materials.

Step 4: Sewing and assembly
- Sew the cut pieces together to make the upper.
- Sew the upper and lining together to make the slipper more comfortable.
- Add laces or other decorations, like buckles or tags

Step 5: Bottom assembly
- Make the sole by molding or bonding, depending on the material (like rubber or EVA).
- Attach the sole to the upper to make a strong, durable slipper.

Step 6 Shaping and molding
- Shape the slipper to fit your foot using a shaping machine.
- Check each slipper to make sure it’s the right size and shape.

Step 7: Quality control
- Check each pair of slippers for quality, including stitching, bonding strength, size, and shape.
- Make sure your slippers meet your factory’s quality standards.

Step 8: Packing
- Pack your slippers the right way to meet the needs of your market and transportation requirements, like boxing or bagging.
How To Deconstruct Slipper Prices ?
Cost of raw materials
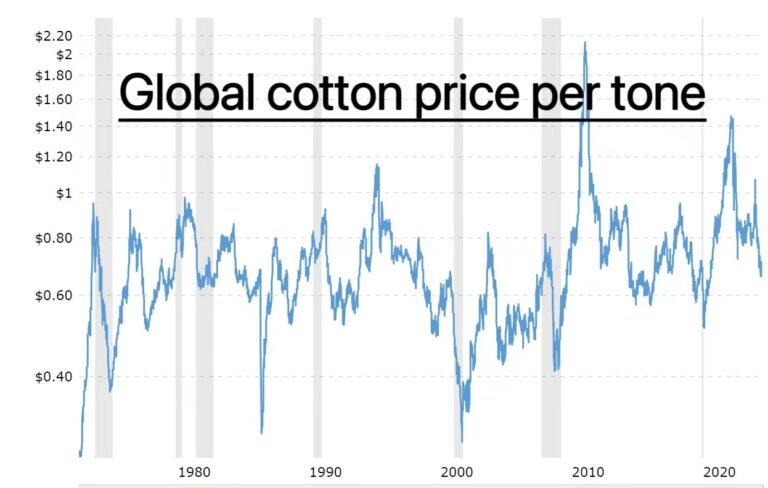
Occupies 30%-50% based on the global market price of cotton fabric and rubber of sole(natural or synthetic.Below chart shows the fluctuation of raw material in recent 2o years.
Production process
Normally the production process cost includes cutting, sewing, packaging, quality control, assembly etc.
Especially for sewing and assembly, this is usually a very labor-intensive step, if you’re making high-quality slippers with complicated designs or doing fine work. Labor is one of the biggest costs in a lot of countries, especially countries with high labor costs.
Labor costs
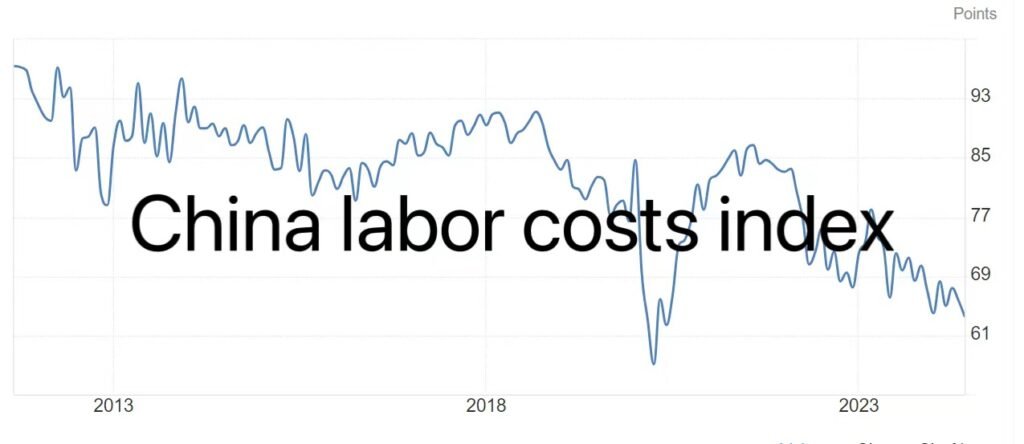
Depends on the geographic distribution in China. The southern area is much expensive against northern part, due to the economy, production technology, quality controls etc.
The average labor cost yearly is decreasing based on the info. as below
Design and development
Most cotton slippers are designed exclusively and have patent protection. For example, images of Paul Frank, Disney. If you want to use these special images, you need to ask for an allowance from related companies.
So the design and development cost are not easy to define.
Logistics and Transportation
Based on the different trading terms and way of shipments, the cost are various sharply.
For weight less than 80KG, express is the most cost-saving way for shipping. Air shipping is more suitable for l80KG- 200KG.
If heavier, train / sea delivery will used a lot. But L/T is longer.
Marketing and advertising
Online and offline promotions occupy a big share. For example, Amazon, Ebay, TV ads etc.
Retailer markup
Taxes and other overheads
Different Price Level of Cotton Slipper in China
Regional 1 - Zhejiang Province
Main production areas: Yiwu, Wenzhou, Taizhou, etc.
Features: Zhejiang is an important manufacturing base for light industry in China. Yiwu is especially famous for small commodities, and there is a wide range of cotton slippers available, from low to medium to high end.
Price level: Cotton slippers made in Zhejiang are generally more affordable in the domestic market, especially in Yiwu, where you can get some really low wholesale prices for large quantities. Wenzhou and Taizhou may have slightly higher prices for some products due to design and branding.
Regional 2 - Guangdong Province
Main production areas: Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan, etc.
Features: Guangdong is the center of manufacturing in China, especially for shoes and clothes. The factories in Guangzhou and Dongguan are technologically advanced and can make high-quality, high-value cotton slippers. Some of these slippers are made for export.
Price level: The price of cotton slippers in Guangdong can vary a lot depending on quality and brand. You’ll pay more for high-end slippers, but regular slippers cost about the same or maybe a little more than they do in Zhejiang. Overall, because of the manufacturing and logistics advantages in Guangdong, the prices for cotton slippers in the local market are competitive.
Regional 3 - Fujian Province
Main production areas: Quanzhou, Jinjiang, etc.
Features: Fujian has a long history in shoe manufacturing. Quanzhou and jinjiang are famous for sports shoes, but they also make a lot of slippers and cotton slippers. The companies here sell to both the domestic and overseas markets, so you can count on the quality and design being good.
Price level: Cotton slippers made in Fujian are moderately expensive in the domestic market. Some of them are branded and priced higher. They aim at the middle to high-end market.
Regional 4 - Hebei Province
Main production areas: Baoding, Shijiazhuang, etc.
Features: Hebei’s shoe industry mainly serves the northern market. Cotton slippers there are warm, especially for winter. Most of the companies are small or medium-sized businesses.
Price level: Cotton slippers made in Hebei are generally cheap and are made for the low-end market. They might be more popular in the north because they’re made for cold weather.
Regional 5 - Shandong Province
Main production areas: Qingdao, Weifang, Linyi, etc.
Features: The shoe manufacturing industry in Shandong has grown quickly in recent years. Some areas focus on exporting, but cotton slippersare mainly sold in China.
Price level: Cotton slippers made in Shandong have a moderate price.The quality is stable, and they’re a good value for the money.
Material

Wool
Wool is one of the oldest materials used to make slippers. People have used wool to make slippers for a long time. It’s soft and warm. Wool comes from the fleece of sheep. You can use wool just like it is, or you can treat it and weave it into different things
Advantages:
- Thermal Regulation: Wool is a great material for making slippers because it keeps your feet warm when it’s cold outside and cool when it’s warm outside. That makes it good for slippers any time of the year.
- Moisture-Wicking: Wool can absorb moisture without feeling damp, which helps to keep feet dry and comfortable.
- Durable: High-quality wool is very resilient. It keeps its shape and doesn’t wear out very easily.
- Eco-Friendly: Wool is good for the environment because it breaks down (biodegrades) and comes back (renews). That means you can sell wool slippers to people who care about the environment.
Cotton
Cotton is another material you can use to make slippers. People use cotton to make lightweight slippers you wear indoors. Cotton is great for people who live in places where it’s warm most of the time.
Advantages:
- Breathability: Cotton is highly breathable, allowing air circulation that helps prevent sweaty feet.
- Softness: It provides a soft and comfortable feel against the skin, making it a favorite for sensitive skin.
- Affordability: Cotton is generally less expensive than wool or leather, making it an attractive option for mass-market slippers.
- Machine Washable: Cotton slippers can usually be cleaned easily, which appeals to consumers looking for low-maintenance footwear.


Faux Fur
Faux fur is a material people use to make slippers. People like faux fur because it looks and feels like real fur, but it’s not made from real animals. People use faux fur to make fancy, high-end slippers.
Advantages:
- Softness: Faux fur provides a plush, ultra-soft texture that consumers find highly comfortable.
- Ethically Sourced: People who love animals and don’t want to wear them like faux fur. That’s why you can sell faux fur slippers to people who don’t like to wear real fur.
- Visual Appeal: Faux fur looks cool. When you put faux fur on your slippers, people will think they’re cool, too.
Leather
Leather is another material people use to make slippers. People like leather slippers because they last a long time and look fancy. You can sell leather slippers to people who want slippers that last a long time and look nice.
Advantages:
- Durability: Leather is one of the most durable materials available. High-quality leather slippers can last for years if properly cared for.
- Aesthetic Appeal:When you put leather on your slippers, they look fancy and expensive.
- Comfort Over Time: When people wear leather slippers, the leather bends and shapes to their feet. That makes them more comfortable.


Faux Leather
Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is often used as an alternative to genuine leather. It offers a similar look at a lower cost and without the ethical concerns surrounding animal products.
Advantages:
- Affordable: Faux leather is good to use because it looks like leather, but it doesn’t cost as much money. That means you can sell faux leather slippers to more people because they cost less money.
- Vegan-Friendly: As it does not involve the use of animal products, faux leather appeals to vegan and environmentally-conscious consumers.
- Easy to Clean: Faux leather is typically easy to wipe clean, requiring less maintenance than genuine leather.
Memory Foam
While not a traditional fabric, memory foam is increasingly used in the footbeds of slippers to enhance comfort. It’s a polyurethane material known for its ability to conform to the shape of the foot.
Advantages:
- Comfort: Memory foam provides exceptional cushioning, making it ideal for consumers seeking superior comfort and foot support.
- Shock Absorption: Memory foam is a special kind of foam you can put in your slippers. When you walk, the foam squishes down and then pops back up. This makes your slippers more comfortable to wear.
- Versatility: Memory foam is a foam you can use to make your slippers feel nice. You can put memory foam inside your slippers along with other materials like cotton or wool. That way, your slippers will feel better, and they’ll still look nice

How to import
1.United States Standard:
The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has a standard (16 CFR Part 1610) for the flammability of textiles, including cotton slippers. Requirements: Textiles have to be flame retardant to keep them from
burning up fast when they touch a flame. The U.S. also has rules about dangerous chemicals in textiles. For example, 16 CFR Part 1303 limits lead and says products have to be nontoxic. The rules for children’s product are really strict
2.European Union
Standard: The European Union (EU) has rules about chemicals in textiles called the REACH Regulation (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals).
Requirements: The EU doesn’t want chemicals in textiles that hurt you, like phthalates, azo dyes, or heavy metals. They have special rules for children’s products about small parts and toxic stuff. The EN 14878 standard tells you how to make flame retardant sleepwear for kids. The
rules for slippers might not be as strict, but you still need to be safe.
3.Japan
Standard: Japan has the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) and the
Japanese Consumer Product Safety Law. They want textiles to be safe. Requirements: The JIS L 1031 standard tells you how to make flame-retardant textiles. Japan also has rules about chemicals in textiles. They don’t want formaldehyde or heavy metals in textiles. You have to pass tests for these standards if you want to sell stuff in Japan.
4.Canada
Standard: The Canadian Health Products Act and Textile Regulations (Textile Flammability Regulations, SOR/2011-22) tell you how to make safe textiles. Requirements: Canada has rules for flame retardancy, especially for sleepwear and other stuff for kids. They also don’t want bad chemicals in textiles. They have rules about dyes and heavy metals.
5.Australia
Standard: Australia has the AS/NZS 1249 standard for the flammability of textiles, especially kids’ sleepwear.
Requirements: The standard is mostly for clothes, but you still have to meet the general rules for textiles to be safe and, in some cases, flame retardant.
1. European Union
Requirements: The European Union takes sustainability and environmental requirements very seriously, and many consumers and retailers will require textiles (including cotton slippers) to be certified as environmentally friendly, e.g. organic cotton (GOTS) or EU Ecolabel.
Related certifications:
GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard): Requires textiles to contain at least 70% organic fibers and that the entire production process meets strict environmental and social standards.
EU Ecolabel: Covers the entire life cycle of the product, from raw materials to production, use and disposal, and requires that the impact on the environment be minimized.
2. United States
Requirements: In the U.S. market, organic certification and sustainable production certification are becoming increasingly important for textiles, especially among high-end and environmentally conscious consumers.
Related certifications:
GOTS: Similar to the EU, the US market recognizes GOTS certification, which is particularly common for organic cotton slippers.
OEKO-TEX Standard 100: This is another widely accepted certification. Although not organic, it ensures that the product is free of hazardous substances and follows environmental standards in production.
3. Japan
Requirements: The Japanese market has very strict product quality and environmental requirements, and consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental performance and sustainability of products.
Relevant certifications:
GOTS: The Japanese market recognizes the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and requires some textile products to comply with this standard.
Japan Organic Cotton Association (JOCA) certification: certification for organic cotton products, to ensure that the product from raw materials to the production process in line with Japan's organic standards.
4. Canada
Requirements: Canada focuses on environmental protection and sustainable development, and consumers and retailers have an increasing demand for environmental certification.
Related Certifications:
GOTS: The Canadian market accepts and promotes GOTS certification, especially for organic textiles.
OEKO-TEX: This certification is also prevalent in Canada and ensures that textiles meet international environmental standards.
5. Australia
Requirements: Australian consumers are increasingly concerned about sustainable and environmentally friendly products, and the market demand for environmentally certified products is growing significantly.
Related certifications:
GOTS: A widely accepted standard, especially in the field of organic textiles.
Australian Certified Organic (ACO): Organic certification specific to Australia, ensuring that products meet Australian organic standards.
6. Nordic countries
Requirements: Scandinavian countries such as Denmark, Sweden and Norway have extremely high requirements for environmental protection and sustainability, and many retailers require textiles (including cotton slippers) to meet environmental certification.
Related certifications:
Nordic Swan Ecolabel: This is an eco-label widely used in the Nordic region to ensure that products have a minimal impact on the environment.
GOTS: In the Nordic countries, there is also a growing number of textile products with GOTS certification, which ensures organic and environmental attributes.
1. United States
Standards: The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) regulates safety standards for children's products.
Major regulations:
Chemical Safety: Under the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA), there are strict limits on the amount of lead and phthalates (phthalates) in children's products. The total lead content in children's products must not exceed 100 ppm (parts per million) and phthalates must not exceed 0.1%.
Flammability: 16 CFR Part 1610 establishes flammability requirements for children's textiles to prevent products from burning quickly, especially for pajama-type products that need to meet more stringent flame retardant standards.
Small Parts: Children's products must not contain small parts that can be easily dislodged to prevent swallowing or choking hazards for children.
Labeling and Certification: All children's products must be tested by a third-party laboratory and labeled with the Children's Product Certificate (CPC).
2. European Union
Standards: The European Union regulates children's products through the Toy Safety Directive (2009/48/EC) and the REACH Regulation.
The main regulations:
Chemical Safety: REACH Regulation strictly limits the use of hazardous substances such as heavy metals, azo dyes and phthalates. The level of chemical substances in children's products must be within the specified safety limits.
Physical and mechanical safety: The EN 71-1 standard specifies physical and mechanical safety requirements, such as preventing sharp edges, small parts, etc., from causing injury to children.
Flammability: The EN 14878 standard addresses the flame retardancy of children's nightwear, but some children's slippers may also need to comply with the relevant fire resistance requirements.
Labeling: All children's products sold in the EU must comply with the CE marking requirements, indicating that the product meets EU safety standards.
3. Japan
Standards: Children's products are regulated in Japan under the Consumer Goods Safety Law and the JIS Standards.
The main regulations:
Chemical safety: Japan has strict restrictions on formaldehyde and heavy metals in textiles, especially for children's products, which are required to be lower than the safety thresholds for adult products.
Physical safety: For children's products, Japan requires that small parts that can easily fall off or break be avoided in the design and manufacturing process to reduce the risk of choking.
Labeling: Product labels must clearly indicate information such as material composition and tips for safe use.
4. Canada
Standard: Canada's Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA) and Textile Flammability Regulations (SOR/2011-22) have strict regulations for children's products.
The main regulations:
Chemical Safety: Canada restricts the content of hazardous substances such as lead and phthalates in children's products, requiring strict compliance with the Hazardous Products Act.
Flammability: The Textile Flammability Regulations require that children's nighttime clothing and textiles must pass a flammability test to ensure that they do not burn quickly upon contact with an ignition source.
Physical safety: Small parts, cords and straps must not be designed to pose a potential risk to children.
5. Australia
Standards: Australia's Consumer Goods Act and AS/NZS 1249 standards regulate children's products.
The main regulations:
Chemical safety: Australia has strict restrictions on harmful chemicals such as lead and phthalates in children's products and requires compliance with non-toxicity standards.
Flammability: Children's nighttime clothing and textiles need to meet the flame retardant requirements of the AS/NZS 1249 standard to ensure that they are not easily combustible in the event of contact with an ignition source.
Physical safety: Small parts and design safety are also mandatory requirements to prevent children from being injured or suffocated.
6. China
Standards: China's National Technical Code for Basic Safety of Textile Products (GB 18401) and related children's product standards regulate children's textiles.
The main provisions:
Chemical safety: The limits of formaldehyde content, pH value, heavy metals and azo dyes in children's products are stipulated to ensure that the products are non-toxic and harmless.
Physical safety: children's clothing and textiles must not contain small parts that can be easily swallowed by children, and string design is also subject to strict requirements.
Flammability: Although general slippers are not required to be flame-retardant, certain special-purpose children's products are still required to meet flame-retardant standards.
1. United States
Certification Requirements:
CPSIA Certification: If cotton slippers are designed for children, they need to comply with the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA), including lead content limits and third-party testing certification.
Labeling Requirements: All imported textiles, including cotton slippers, must comply with U.S. labeling regulations that identify the manufacturer, country of origin, material composition and cleaning care instructions.
FLAMMABILITY TESTING: Imported cotton slippers may be required to pass a flammability test under 16 CFR Part 1610, especially if they are designed for a specific use such as pajamas.
Tariff Policy:
Import tariff rates for cotton slippers are typically around 10-20%, but the exact rate depends on the product's subcategory and country of origin.
Trade policies may impose additional tariffs on products from certain countries, especially during the U.S.-China trade dispute, when tariffs had been imposed on certain Chinese-made products.
2. European Union
Certification requirements:
CE Marking: If the cotton slippers have any toys or electronic components, they must comply with the CE marking requirements, indicating that the product meets EU safety, health and environmental standards.
REACH regulation: Imported cotton slippers must comply with the REACH regulation, especially the restrictions on chemicals (e.g., phthalates, azo dyes, etc.) to ensure that the product does not contain hazardous substances.
Eco-labeling: Although not a mandatory requirement, obtaining an EU eco-label can help products be more competitive in markets with higher environmental awareness.
Tariff policy:
Cotton slippers imported from countries outside the EU are usually subject to tariffs ranging from 2.5% to 5%, depending on the product's HTS code and country of origin.
The EU has Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with a number of countries and regions, and products that comply with the rules of origin may be eligible for tariff preferences or duty-free treatment.
3. Japan
Certification Requirements:
JIS Standards: Japan's Industrial Standards (JIS) have requirements for imported cotton slippers, particularly with regard to the physical safety of the product, the content of chemical substances, and flame retardancy.
Harmful substances restrictions: Japan has strict restrictions on formaldehyde, heavy metals, etc. in textiles, and imported products need to meet these requirements.
Country of origin marking: All imported goods must be marked with the country of origin, and labeling information must be provided in Japanese.
Tariff Policy:
Japan's tariffs on imported textiles are usually low, with tariffs on cotton slippers ranging from about 3% to 5%, but the exact rate depends on the product category and the country of origin.
Japan has Economic Cooperation Agreements (EPAs) with certain countries that may provide tariff relief for eligible products.
4. Canada
Certification Requirements:
CCPSA Certification: Imported children's cotton slippers must comply with the Canadian Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA) to ensure that they do not contain hazardous substances and meet physical and chemical safety standards.
Labeling Requirements: Products must comply with the Textile Labeling Act, including detailed descriptions of ingredients, country of origin and care instructions.
Flammability Standards: For certain specific products, compliance with Canada's textile flammability standards may be required.
Tariff Policy:
Canadian tariffs on textile imports typically range from 5% to 18%, depending on product classification and country of origin.
Canada has free trade agreements with several countries, such as the CUSMA (USMCA) with the United States and Mexico, and eligible products may be entitled to preferential tariff treatment.
5. Australia
Certification Requirements:
AS/NZS standards: Imported cotton slippers need to comply with Australian and New Zealand standards, especially children's products need to comply with flame retardant and non-toxicity requirements.
Labeling Requirements: All imported products must comply with Australian labeling requirements, including ingredients, country of origin and instructions for use.
Tariff Policy:
Australia's tariffs on imported cotton slippers generally range from 5% to 10%.
Australia has Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with several countries, and eligible products may be eligible for tariff reductions or exemptions.
6. China
Certification Requirements:
CCC Certification: While the cotton slippers themselves may not require CCC certification, if the slippers contain electronic components (e.g., a heating function), they will need to pass China's Compulsory Product Certification (CCC).
Labeling Requirements: All imported products must comply with China's mandatory labeling requirements, including Chinese labels, which need to indicate the ingredients, country of origin, manufacturer and other information.
GB 18401 Standard: Textiles must comply with China's National Technical Code for Basic Safety of Textile Products, especially in terms of chemical substance content and physical properties.
Tariff Policy:
China's tariffs on imported textiles usually range from 10% to 20% depending on product classification.
China may offer preferential tariff treatment for products from certain countries of origin, particularly those countries with which China has signed free trade agreements.
1. European Union
Requirements: In the EU, although ISO 9001 certification is not legally mandatory, it is widely recognized as a condition of entry into the EU market. Especially when working with large retailers and brands, suppliers with ISO 9001 certification are more likely to gain trust and contracts.
Application scenarios: Some EU member states may require suppliers to hold ISO 9001 certification for government procurement programs or specific industries, such as medical equipment and construction products.
2. United States
Requirements: In the United States, ISO 9001 certification is not mandatory by law, but many large companies and retailers, including Walmart and Amazon, tend to work only with suppliers that are ISO 9001 certified.
Application scenarios: ISO 9001 certification may be a requirement especially when bidding for tenders or participating in important parts of the supply chain. In addition, the U.S. military and some government procurement programs may also require suppliers to hold such certifications.
3. Canada
Requirements: In Canada, ISO 9001 certification is widely used in the industrial and manufacturing sectors. Although not mandatory, many retailers and distributors require their suppliers to hold this certification, especially in the consumer goods and electronics industries.
Application Scenario: ISO 9001 certification can be used as proof of quality and compliance when participating in government contracts or in the supply chain of multinational companies.
4. Japan
Requirements: Japan places great emphasis on quality management systems and ISO 9001 certification is widely used in the manufacturing industry. Although not legally mandatory, many Japanese companies, including small and medium-sized enterprises, give preference to ISO 9001 certified companies when selecting suppliers.
Application scenario: In the textile and consumer goods industry, holding ISO 9001 certification may be a necessity when working with large retailers and export markets.
5. China
Requirements: In China, ISO 9001 certification is an important standard for quality management. Although it is not mandatory for domestic sales, holding ISO 9001 certification is seen as a competitive advantage, or even a necessity, for exporters, especially for those exporting to European and American markets.
Application scenario: For Chinese companies that wish to enter the international market or work with multinational companies, ISO 9001 certification is often one of the thresholds for participation in the global supply chain.
6. Australia
Requirements: Australia encourages companies to follow the ISO 9001 quality management standard, especially in the manufacturing and construction industries. Although not mandatory, many customers and partners require suppliers to hold ISO 9001 certification.
Scenario: In Australia, companies holding ISO 9001 certification have an advantage when participating in government tenders and large commercial contracts.
7. Middle East and North Africa
Requirements: ISO 9001 certification is widely accepted in many countries in the MENA region, particularly in countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Egypt. Although not a mandatory requirement, ISO 9001 certification is seen as an important assurance of quality and credibility for those wishing to enter these markets or work with large local companies.
Application scenario: Many international companies operating in the MENA region require their suppliers and partners to hold ISO
1. European Union
Language requirements:
The information on the label must be in the official language of the country in which it is sold, usually the main language or multiple official languages of that country. For example, a label for slippers sold in France must be in French, a label sold in Germany must be in German, etc.
If the product is sold in more than one EU country, the labeling will usually need to be multilingual to ensure that the consumer understands all the necessary information.
Information requirements:
Country of origin: the country of origin of the product must be clearly indicated.
Material composition: the composition of all the main materials must be listed (e.g. 100% cotton).
Washing and care instructions: International washing symbols are usually used and an explanation in the language of the country needs to be provided.
Size identification: the size or range of application of the product needs to be indicated.
Manufacturer information: This includes the name and address of the manufacturer or distributor.
2. United States
Language Requirements:
The information on the label must be displayed in English. For some specific markets, such as Puerto Rico, Spanish may also be required.
Information Requirements:
Country of Origin: Under the Textile Fiber Product Identification Act (TFPIA), products must be clearly labeled with the country of origin.
Material Composition: The composition of the main fiber material must be listed by percentage (e.g., 80% cotton, 20% polyester).
Care instructions: must include clear washing and care instructions, which usually need to be in text form and may include icons.
Manufacturer information: the name and address of the manufacturer, importer or distributor must be indicated.
Size and use: the size and applicable use of the product needs to be indicated.
3. Canada
Language Requirements:
Under the Consumer Goods Labeling Act, labels must be in both English and French, due to the fact that Canada is a bilingual country.
Information Requirements:
Country of Origin: The country of origin of the product must be stated on the label.
Material Composition: The material composition needs to be clearly listed, usually as a percentage.
Care instructions: care instructions must be provided in both English and French, and the use of universal washing symbols is also an accepted practice.
Manufacturer Information: The name and address of the manufacturer or importer must be included.
Size identification: indicates the size or range of application of the product.
4. Japan
Language Requirements:
The information on the label must be displayed in Japanese, which is a legal requirement.
Information Requirements:
Country of origin: the country of origin of the product must be indicated.
Material Composition: The composition of the product must be listed in detail, especially the composition and proportion of textile materials.
Care instructions: Clear washing and care instructions are required, usually using international symbols plus Japanese explanations.
Manufacturer information: This includes the name and contact information of the manufacturer and importer.
Other: additional information may be required, such as warnings to prevent misuse or precautions for use applicable to certain specialty products.
5. China
Language Requirements:
Labels must be in simplified Chinese, especially for products sold in the Chinese market.
Information Requirements:
Country of origin: The country of origin of the product must be clearly labeled.
Material Composition: Must list the proportion of the composition of the main materials.
Care instructions: Care instructions for washing, drying and ironing need to be included and detailed in Chinese.
Manufacturer information: the name, address and contact information of the manufacturer or importer need to be included.
Size identification: need to clearly indicate the size or scope of application of the product.
6. Australia
Language requirements:
Label information must be displayed in English to meet Australian language requirements.
Information Requirements:
Country of origin: The country of origin of the product must be indicated.
Material Composition: The composition of all major materials needs to be listed.
Care instructions: Care instructions need to be included on the label, using the universal symbol for washing and supported by textual descriptions.
Manufacturer Information: Include the name and contact information of the manufacturer or importer.
Get Free Quote
Contact us to get a free quote and more expertise about custom aluminum extrusion. Your project will meet a right solution with Apextrusion.
- Qingchun Road,Xiaolin Town,Ningbo,Zhejiang Province,China
- chris@cottonslippper.com
- 0086 183 687 28228
